Main Page | Knowledge base | Geophysics | Georadar | GPR Profiling
GPR PROFILING
GPR profiling technique, also called reflection profiling, is the simplest technique for GPR. It involves analysis of structure of the medium using separate sections, where the location is designed before start of the measurement. Theirs positions are adjusted directly during the GPR acquisition depending on the field’s conditions. Given the fact that during the georadar surveys signal dampens with depth increasing and clay minerals contribute to this phenomenon as well. As a result, the effectiveness of GPR strongly restrict silty clay grounds and saturation of soil water.
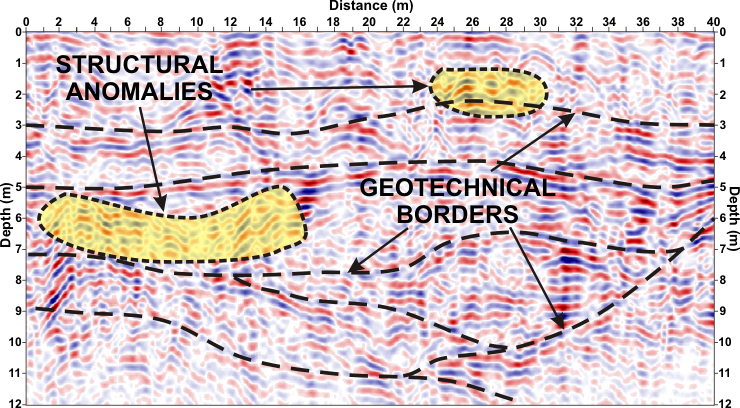
Profiling technique is ideal for the detection geotechnical borders where layers differ from each other by dielectric constant. The lower frequency georadar antennas where depth range is greater but vertical resolution is less, are used to survey the geological and exploration of larger objects at a considerable depth (up to several meters ppt). Accordingly, high frequency GPR antenna with a small range but high resolution is used to detect geotechnical borders in applications for construction of transport infrastructure such as roads, ring roads or highways.
The main advantage of the shallow georadar profiling unlike other geophysical methods, is relatively good reflection of the structure of the medium. It shows the structural anomalies of any kind relative to the surroundings. This may be a zone of fractures, faults, rocks, buildings, crypts, infrastructure, or may indicate the place of disturbed soil.
In many cases, there isn’t a precise profiling the medium without the need for multiple antennas with different parameters. Their mutual correlation also allows for more accurate exclusion of interference. There are different GPR systems available that have more than one antenna. In carrying out such a set in profiling, there is not necessary to perform several overlapping profiles of different antennas, because that kind of multi-georadar system do it in one pass.
A more advanced version of this geophysical method is GPR mapping. In many cases searching for underground facilities or other georadar analysis often requires examination of some area. Mapping by performing a series of parallel profiles will interpolate data between successive profiles, and the results are presented in the form of a transparent map at any level of the depth. More…
Examples of application of the georadar method using GPR profiling:
- Location of objects, such as tunnels, shallow excavations (shafts, mine roadways and other types of underground structures like chambers, collectors, tanks, concrete slabs and columns, foundations ,piles ,etc.). More…
- Planning and maintenance of cable and pipeline,
- Examination of the structures of bridges, viaducts, ceilings and walls,
- Diagnostics and substrate surface: roads ,highways ,railways ,airport runways and aprons. More…
- Evaluation of the deployment of primers such as gravel. More…
- Detection of mining voids and karst caverns, sinkholes and subsidence. More…
- Classification of the substrate, delamination and segmentation decks. More…
- Analysis of the position of the water table,
- Shallow lithological and stratigraphic analysis. More…
- Characteristic of system cracks of rocks and concrete,
- Support for archaeological works.










